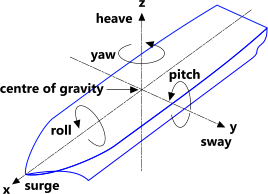
An intertial measurement unit (IMU) is used to measure the orientation of an object in free space. We parameterize this orientation as the quantities roll, pitch, and yaw. In our case, the yaw is relative to north (i.e. a boat heading of due north has a yaw of 0 degrees). The roll and pitch are not needed by the main navigation algorithm, but may be useful for applications like computer vision where stabilization may be required.
Hardware Configuration
The IMU that we use, the Yost Labs 3-Space Sensor Embedded LX, uses I2C protocol to communicate with the microcontroller. The pinout is as follows:
| IMU | Microcontroller |
|---|---|
| 6. VIN | Power (3.3 or 5V) |
| 3. GND | Ground |
| 1. SCL | SCL |
| 2. SDA | SDA |
It is also possible to use other communication protocols to interact with this IMU model (USB, SPI, or UART), but I would advise against this since the I2C bus is already being used by other sensors and grouping multiple peripherals on one bus limits the number of pins taken.
Software Configuration
The specifics of configuring I2C depend on the microcontroller used. The I2C address of the IMU is 0xEE and it supports clock speeds up to 300kHz. The process to read Euler angles (the orientation format that we use) from the IMU is: write the configuration (0x42) and Euler angle (0x01) commands to the IMU, write the request data command (0x43) to the IMU, then read 12 bytes of data from the IMU.
The 12 bytes that are read are of the form: 3 bytes (one float) for pitch, then 3 bytes for yaw, and finally 3 bytes for roll. The floats must be endian swapped (order of the bytes in each float reversed) before they can be usefully interpreted. All of these values are given as radians, so they must also be converted to degrees.
Calibration
The IMU should be calibrated before testing or use in competition. Try to do this in an environment where magnetic interference won’t be a problem (i.e. not around lab equiptment or close to computers). Download the 3-Space Sensor Software Suite and connect the IMU to your computer via USB. In the software suite application, under the sensor tab, select gradient descent calibration and follow the instructions given.